Exhibition dates: 24th November 2012 – 11th March 2013
Louise Bourgeois & Australian Artists
13 October 2012 – 14 April 2013
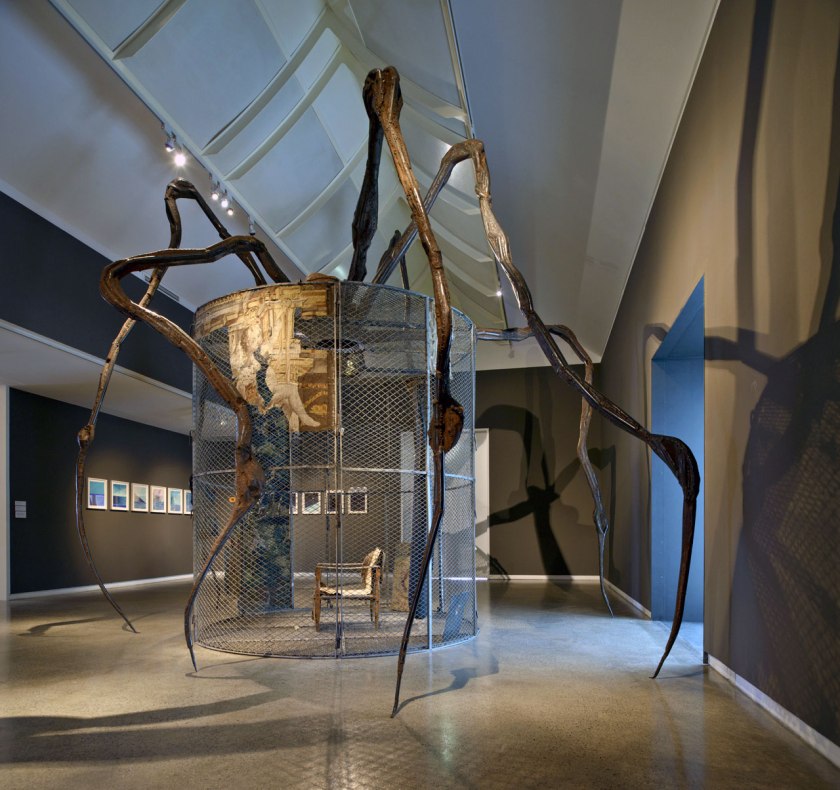
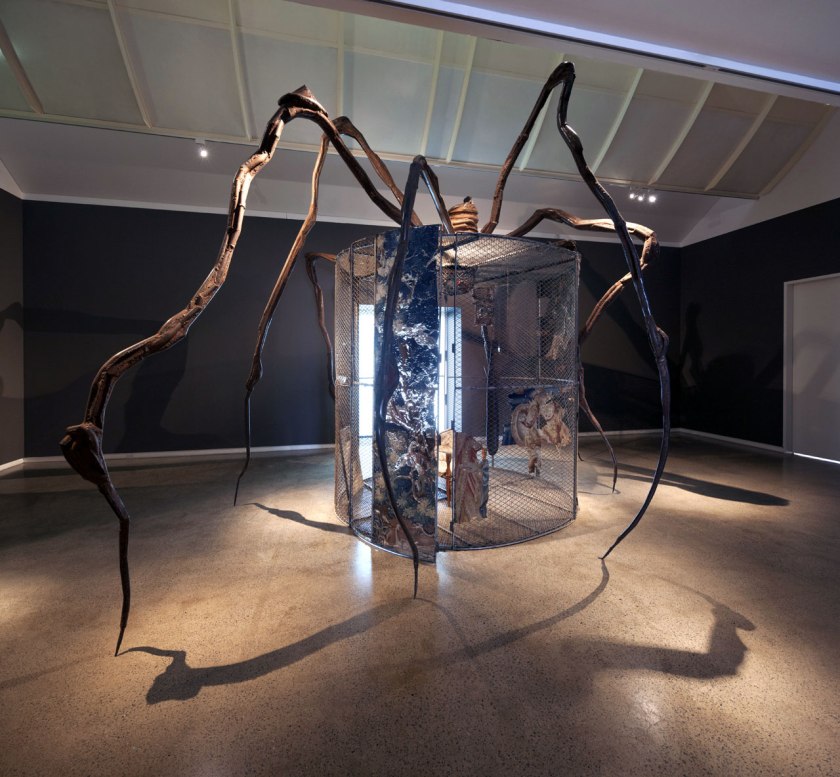
Louise Bourgeois: Late Works installation view
Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne
Photograph: John Gollings 2012
“What counts, our whole purpose, is to try to understand what we are about, to scrutinise ourselves… Every day you have to abandon your past or accept it, and then, if you cannot accept it, you become a sculptor. ”
“The fears of the past were connected with the functions of the body, they reappear through the body. For me, sculpture is the body. My body is my sculpture.”
.
Louise Bourgeois
“What images can art find for depicting femaleness from within, as distinct from the familiar male conventions of looking at it from the outside, from the eye-line of another gender?” Hughes questioned in a commentary that implied no precedents. “… [Her] influence on young artists has been enormous.”
.
Robert Hughes quoted by Annemarie Kiely on the Vogue Living Blog [Online] Cited 28/02/2013 no longer available online
“Yes, there are the oft-told stories of the father and the mistress, but it is Bourgeois’s intense love of her mother and her [mother’s] death that completely transformed her life… The art ultimately became about her never-ending grief… and her continuing desire as a woman. It’s still so potent; not just as a memory, but as a constant.”
.
Jason Smith, Curator, Director and CEO of Heide quoted by Annemarie Kiely on the Vogue Living Blog [Online] Cited 28/02/2013 no longer available online
Tough Love
This is a tough, stimulating exhibition of late works by Louise Bourgeois at Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne. All the main themes of the artist’s work explored over many years are represented in these late works: memory, emotion, anxiety, family, relationships, childhood, pain, desire and eroticism are all present as are female subjectivity and sexuality, expressed through the body. As the quotation above by Bourgeois states, her body became her sculpture.
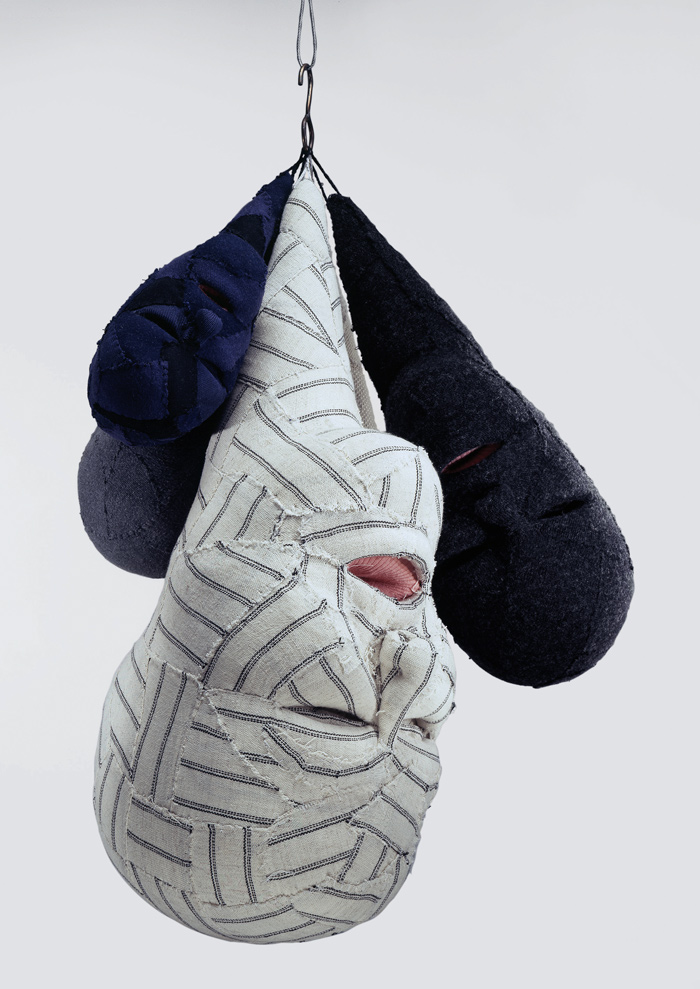
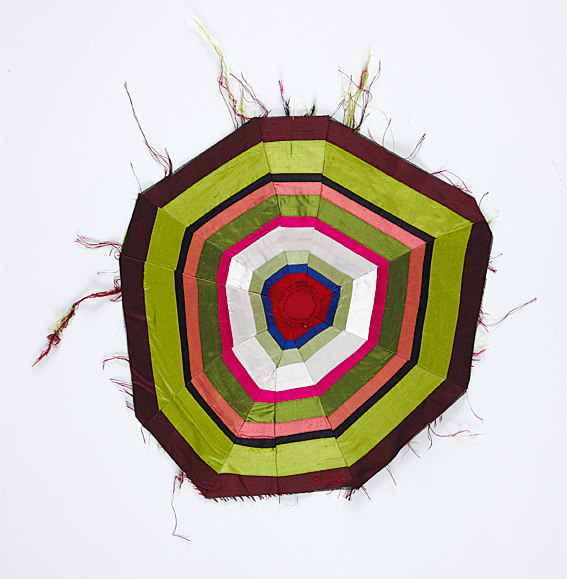
I am no expert on the work of the artist. But what I will try and enunciate are my feelings when viewing the exhibition. Firstly, I thought the drawings by Louise Bourgeois in Heide II were the most magical thing that I saw all day; they seemed to be the well spring of her creativity, the initial thought sketched quickly and imperiously. Secondly, series such as Dawn (2007, below) and The Waiting Hours (2007), assemblages of cut fragments of her dresses and other textiles used to create spiral three-dimensional realities, were the most beautiful, peaceful Zen based works in the exhibition possessing as they did a calm, resolved, mandala-like presence. Lastly, the main group of sculptures were, for me, hard to look at. A series of severed heads, dismembered bodies, tapestry fragments, spiders, bones, an orrery-like planetarium, pendulous objects stuck with needles, kitchen implements and the house brought back memories of my own childhood.
I was born in the late 1950’s to a mother who didn’t really want to have children, to a mother who was already being beaten up by an abusive husband before she was even married, who lived on a remote, isolated farm in the middle of nowhere. I can’t imagine what my mother went through in those early years raising two children – with no hope of help or escape, with no women’s refuge to flee to, stuck there doing her best to protect her children and herself from a violent, mentally ill man. You cannot imagine the torment I went through for the first 18 years of my life, trying to protect my mother when I was old enough, creating my own worlds to escape the reality of the present (which is why I probably became an artist, to still create my own worlds). There were good times at Christmas and bonfire night, but the best part was growing up on the land, learning the rhythms of nature, learning to drive on a tractor and combine harvester, but always in the back of your mind was the instant of abuse lurking around the corner, the inherent violence of life. It is only now, as I have grown older, that I can truly appreciate the dire predicament that my mother was in and acknowledge a profound sense of gratitude towards her protection of me as a baby and child.
That is why this exhibition is, for me, tough love. The emotions of Bourgeois’ sculptures are close to the bone. As Jason Smith observes, “Bourgeois saw her mother as rational, patient and stoic in her nurturing, in contrast to the temperament of her father whom she regarded as irrationally emotional, unreasonable and capable of psychological cruelty. Bourgeois became aware at an early age that she was living in a time and social environment in which women and their identities were subordinate to men.”As Bourgeois says of the spider (her mother), “she was deliberate, clever, patient, soothing, reasonable, dainty, subtle, indispensable, neat and as useful as a spider. She could also defend herself, and me.” This is what my mother did as well, at great cost to herself.
Bourgeois’ work gives me an overall feeling of immersion in a world view, one that transcends the pain and speaks truth to power. Bourgeois confronted the emotion, memory or barrier to communication that generated her mood and the work. She observed, “My art is an exorcism. My sculpture allows me to re-experience fear, to give it a physicality, so that I am able to hack away at it.” By weaving, stitching and sewing Bourgeois threaded the past through the present and enacted, through artistic performance, a process of repair and reconstruction, giving meaning and shape to frustration and suffering. I have not been so lucky. My mother refuses to discuss the past, will not even come close to the subject for the pain is so great for her. I am left with a heaviness of heart, dealing with the demons of the past that constantly lurk in the memory of childhood, that insistently impinge on the man I am today. Louise Bourgeois’ sculptures brought it all flooding back as the work of only a great artist can, forcing me to become an ethical witness to her past, my past. A must see exhibition this summer in Melbourne.
Dr Marcus Bunyan
.
Many thankx to curator and Director Jason Smith and Heide Museum of Modern Art for allowing me to publish the photographs in the posting. Please click on some of the photographs for a larger version of the image.
Louise Bourgeois: Late Works installation view
Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne
Photograph: John Gollings 2012
“The friend (the spider – why the spider?) because my best friend was my mother and she was deliberate, clever, patient, soothing, reasonable, dainty, subtle, indispensable, neat and as useful as a spider. She could also defend herself, and me.”
.
Louise Bourgeois, from Ode to my Mother, 1995
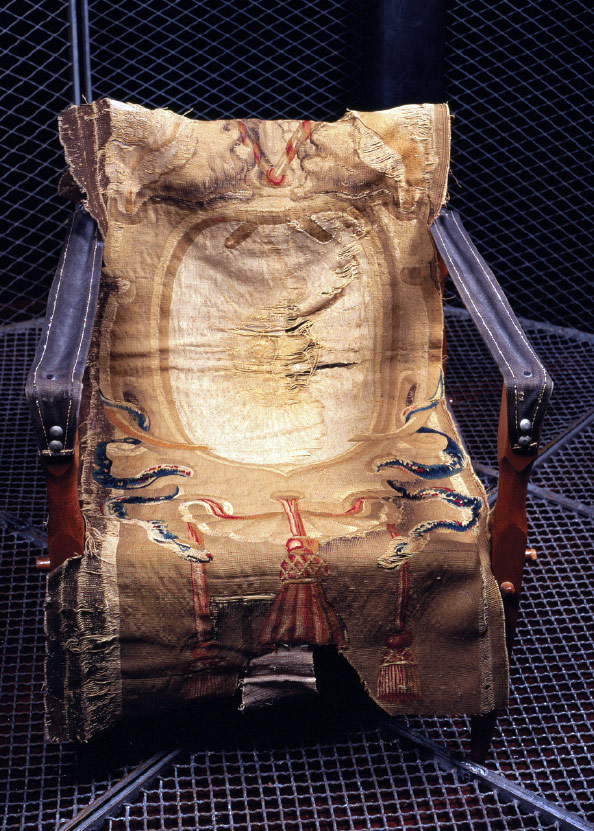
Louise Bourgeois (French-American, 1911-2010)
Spider (detail)
1997
Steel, tapestry, wood, glass, fabric, rubber, silver, gold, bone
449.6 × 665.5 × 518.2cm
The Easton Foundation, New York, NY
Photograph: John Gollings 2012
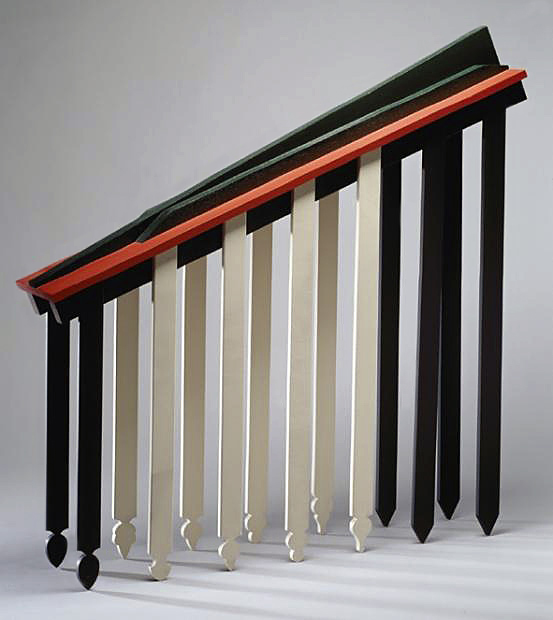
Louise Bourgeois (French-American, 1911-2010)
Dawn (detail)
2007
Fabric book, 12 pages
12 1/4 x 9 3/4 inches each
Around 1996, aged 85, Bourgeois began to mine her closets for the garments and textiles that she had worn, collected and stored over a lifetime, and use them to make sculpture and ‘fabric drawings’, continuing her lifelong recall and articulations of familial dysfunction, desire and fear, anger and remorse, isolation and connectedness. In the recycling and reconstruction of her clothing and collected textiles Bourgeois intensified her work’s expression of the human body and of life’s episodes (those as daughter, wife, mother, woman, artist). The materiality of these works testifies to the impression of Bourgeois’ past on her psyche and on reparative acts of making through which her past was reconciled in her present. The beauty of the past for Bourgeois resided in the nurturing, repairing, fortifying and protective tendencies of her mother, which she aligned with the processes of stitching and assembling.
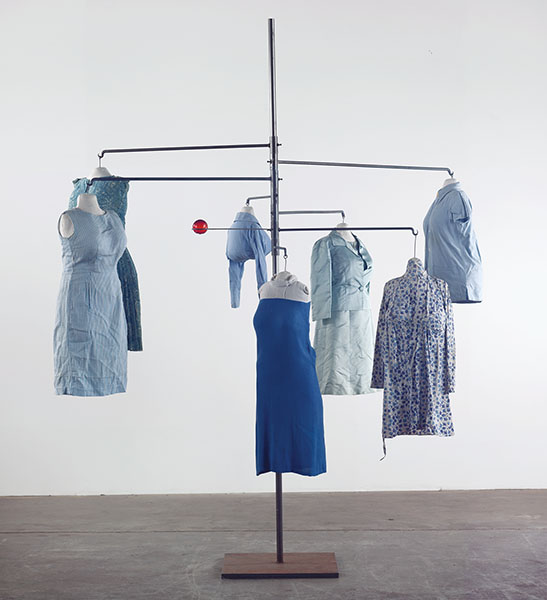
Blue Days (1996) is one of a number of works in which Bourgeois suspended, stuffed and shaped her dresses and shirts, sometimes adding abstract sculptural elements like the red glass sphere that operates here like a nucleus around which the new sculptural bodies circulate. With its intimate relation to the skin and contours of the body, to time and seasons, clothing was used for its power to summon memory: ‘You can retell your life … by the shape, weight, colour and smell of those clothes in your closet. They are like the weather, the ocean, changing all the time.’
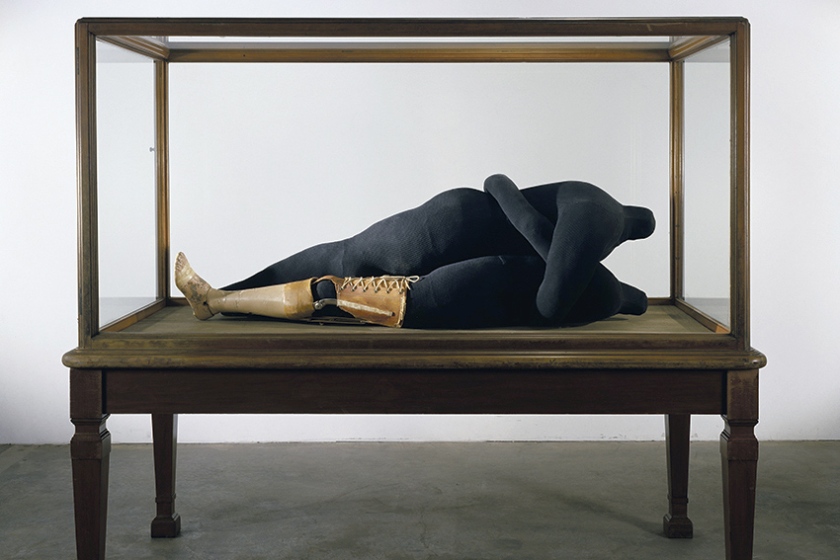
In other works Bourgeois’ fragmented figures and anatomical parts give physical form to anxieties rising from unfulfilled desire, acts of betrayal, losses or thwarted communication. Couple IV embodies the dark confusion of the child happening upon the sexual embrace of the adults. The copulating, decapitated lovers appear as an encased ‘archaeological specimen’ and signal Bourgeois’ fraught obsession not only with the infidelities of her father, but also with sex itself. For Bourgeois there is ‘a fatal attraction not towards one or the other, but to the phenomena of copulation … I am exasperated by the vision of the copulating couple, and it makes me so furious … that I chop their heads [off]. This is it … I turn violent. The sewing is a defence. I am so afraid of the things I might do. The defence is to do the opposite of what you want to do.’
Louise Bourgeois’ practice was an elaborate articulation of an existence in which the sculpting world and the living world were one. Her late works summoned the past and confronted the present, and the passage of time, by using the very garments in which the experiences of her life, loves and longings resided.
Jason Smith, Curator, Director and CEO, Heide Museum of Modern Art. “Louise Bourgeois,” on The Melbourne Review website, November 2012 [Online] Cited 26/02/2013 no longer available online
Louise Bourgeois (French-American, 1911-2010)
Blue Days
1996
cloth, steel, glass
292.1 × 205.7 × 241.3cm
Courtesy Cheim & Read and Hauser & Wirth
© Louise Bourgeois Trust / Licensed by VAGA, New York / Viscopy, Sydney
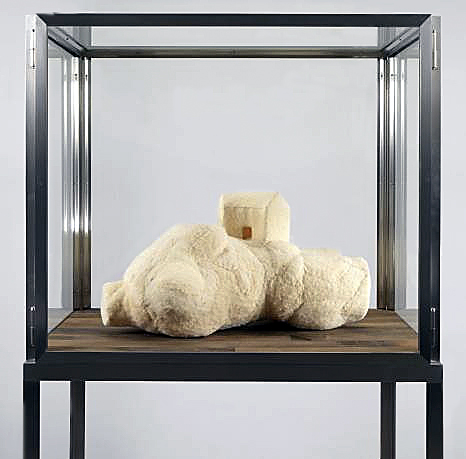
Louise Bourgeois (French-American, 1911-2010)
Femme Maison
2001
fabric, steel
35.6 × 38.1 × 66 cm
Courtesy Cheim & Read and Hauser & Wirth
© Louise Bourgeois Trust / Licensed by VAGA, New York / Viscopy, Sydney
Louise Bourgeois (French-American, 1911-2010)
Femme Maison (detail)
2001
fabric, steel
35.6 × 38.1 × 66cm
Courtesy Cheim & Read and Hauser & Wirth
© Louise Bourgeois Trust / Licensed by VAGA, New York / Viscopy, Sydney
Note that Femme Maison and other artworks are encased in ‘cells’. In one sense, the cell encases and protects the artwork; however, Louise Bourgeois’ intention was to use the cell also as a way of containing the memory held within the work.
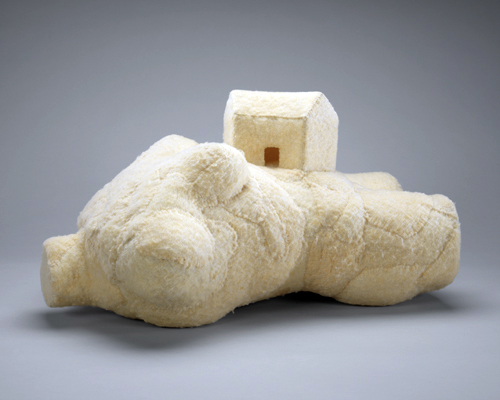
The hybrid form of Femme Maison – with its dual translations to ‘woman house’ or housewife – appeared in drawings, paintings and sculpture, and in degrees of abstraction and figuration, from the mid 1940s onwards. In this key late work the textured fabric affirms the central relationship of woman with the domestic space. Stories of the house and the home defined Bourgeois’ identity. The architectural house and its contents – especially the table, bed and chair – and the familial home and its occupants, were the structures that shaped Bourgeois’ unstable sense of self, and her relationships with others. This work plays on the house literally growing out of the woman’s body (the nurturing mother) or, conversely, pinning her dismembered body to the ground, registering the paralysing power of fear, and recalling a painful childhood.
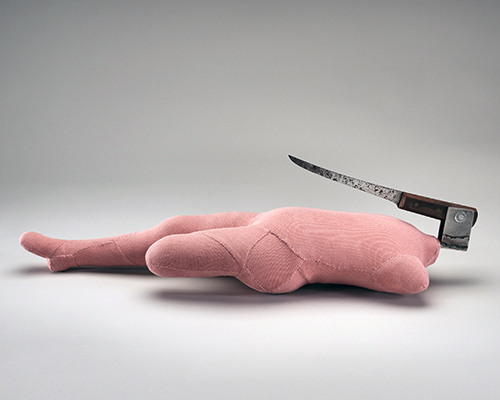
Louise Bourgeois (French-American, 1911-2010)
Knife Figure
2002
fabric, steel, wood
22.2 × 76.2 × 19.1cm
Courtesy Cheim & Read and Hauser & Wirth
© Louise Bourgeois Trust / Licensed by VAGA, New York / Viscopy, Sydney
Louise Bourgeois (French-American, 1911-2010)
Untitled
2002
Tapestry and aluminium
43.2 x 30.5 x 30.5cm
Courtesy Cheim & Read and Hauser & Wirth
Photo: Christopher Burke
© Louise Bourgeois Trust
Louise Bourgeois (French-American, 1911-2010)
Couple IV
1997
fabric, leather, stainless steel, plastic
50.8 × 165.1 × 77.5cm
Courtesy Cheim & Read and Hauser & Wirth
© Louise Bourgeois Trust / Licensed by VAGA, New York / Viscopy, Sydney
Louise Bourgeois (French-American, 1911-2010)
Untitled
2002
Tapestry, aluminium
43.2 x 30.5 x 30.5cm
The Easton Foundation, New York, NY.
Louise Bourgeois (French-American, 1911-2010)
Cinq
2007
fabric, stainless steel
61 × 35.6 × 35.6cm
Courtesy Cheim & Read and Hauser & Wirth
© Louise Bourgeois Trust / Licensed by VAGA, New York / Viscopy, Sydney
Heide Museum of Modern Art is proud to present two major exhibitions featuring the work of Louise Bourgeois. The first, Louise Bourgeois: Late Works includes over twenty, key works direct from the late artist’s studio in New York. The second exhibition, Louise Bourgeois and Australian Artists presents a selection of works by contemporary Australian artists who have been inspired by Bourgeois alongside prints and drawings from her vast graphic oeuvre. Louise Bourgeois (1911-2010) was one of the most inventive, provocative and influential artists of the twentieth century. Although her work has been exhibited extensively overseas, it has rarely been seen in Australia, and only once in significant depth, at the National Gallery of Victoria (NGV) in 1995 in an exhibition curated by then NGV curator Jason Smith. Louise Bourgeois: Late Works focuses on Bourgeois’s use of fabric in sculpture and what she termed ‘fabric drawings’. A preoccupation with memory and time, human relationships, fear and its annihilation, sexuality and the erotic body, are all emphases of Bourgeois’ final works.
Louise Bourgeois: Late Works is the first exhibition in Australia to survey the work of this profoundly important artist since her death in 2010 and has been curated by Jason Smith, now Heide Director & CEO – in close collaboration with the Bourgeois studio, New York – as a follow up to the 1995 exhibition at the NGV. Focusing on the final fifteen years of Bourgeois’ career, the exhibition examines the use of fabric in her works, and includes 18 sculptures, two suites of ‘fabric drawings’, watercolours, embroidered texts and lithographs never before seen in Australia. In the fabric works the processes of deconstructing and reconstructing, are applied to the contents of Bourgeois’ closets. The recycling of her garments, collected textiles and tapestry fragments intensifies her work’s expression of self-portraiture, and the profound personal experiences that defined her life and art.
Fabric was important to Louise Bourgeois, who grew up in her parents’ tapestry making business. In 1996, in her mid-eighties, Bourgeois began to transform the garments and textiles that she had worn, collected and stored over a lifetime into sculptures and ‘fabric drawings’. For her, sewing was an act of healing or reparation, linked to memories of her mother who ‘would sit out in the sun and repair a tapestry or a petit point’, an image of calm amid more distressing family dynamics.
Central to the exhibition is Spider, 1997 one of the Bourgeois’ Cells sculptures which is dominated, enclosed and protected by a gargantuan spider – a recurring and powerful motif in the artist’s work. Bourgeois created her spider sculptures partly in tribute to her mother, saying: ‘Like a spider, my mother was a weaver. Spiders are helpful and protective, just like my mother’. The female body and female subjectivity are concentrations in the exhibition.
The familial, biographical stories that provided life-long fuel for Bourgeois’ art are well known: her parents’ tapestry workshop in which she learnt the value of art as a form of reparation; her father’s public infidelity; her mother’s betrayal and early death; her complex sense of abandonment; her constant analysis of self; her belief in art a form of exorcism and as a potential reconciliation with the past.
Another highlight of the exhibition is the haunting Couple IV 1997, depicting a pair of copulating, and decapitated, lovers. The embracing figures are cast in the black of mourning, and appear as an encased ‘archaeological specimen’ in the vitrine. The work signals Bourgeois’ fraught obsession with the past, the infidelities of her father, and with sex itself.
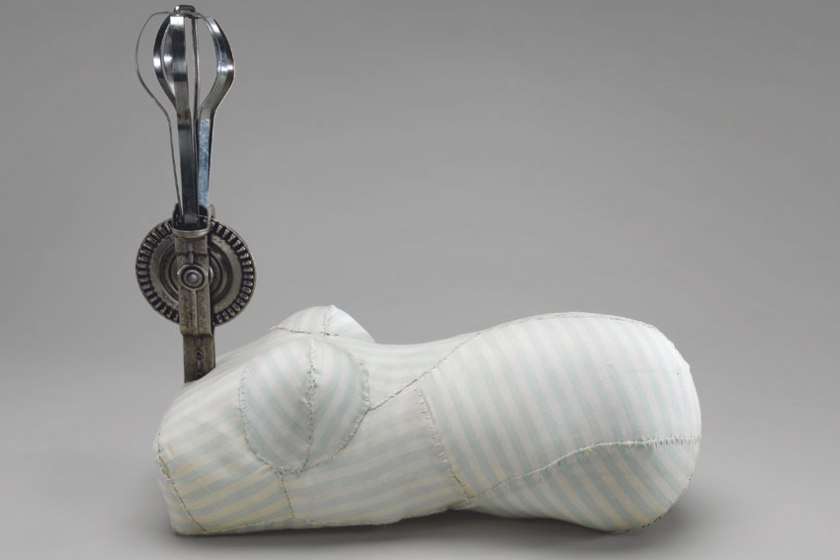
Surrealism and pathos combine in Bourgeois’ smaller, intimate works like Knife figure 2002 and Untitled 2002. Here we see a dark side of the domestic with the knife and the whisk looming threateningly large in relation to the prone, dismembered bodies. In their colouration and homely material qualities they inspire tenderness and protection, yet as with so many of Bourgeois’ bodies, each remains cut off from the world and isolated to deal with its fate.”
Press release from the Heide Museum of Modern Art website
Louise Bourgeois & Australian Artists
This exhibition looks at relationships, both real and imagined, between the art of Louise Bourgeois (1911-2010) and that of ten Australian artists, in the rare context of a solo Bourgeois exhibition at Heide. Some pay direct homage to Bourgeois’ work or consider similar themes, while the connection of others registers more instinctually, on the level of a shared psychological intensity. Many of the works are rooted in memory and emotion, with a core that remains indecipherable – they do not illustrate or explain.
Forged regardless of fashion or fortune, Bourgeois’ oeuvre gave several artists in this exhibition the impetus to use personal subject matter as a creative source in the late 1980s and 1990s, an era when a cool, detached conceptualism dominated. Many share Bourgeois’ subjective focus and use the human body as a vehicle for self-expression, while for others her work’s formal precision and constant reinvention inspire. All respond to the exemplary fusion in Bourgeois’ art between inner compulsion and formal discipline, instinct and intelligence.
The Australian artists are Del Kathryn Barton, Pat Brassington, Janet Burchill, Carolyn Eskdale, Brent Harris, Joy Hester, Kate Just, Patricia Piccinini, Heather B. Swann.
Statement from the from the Heide Museum of Modern Art website
Janet Burchill (Australian, b. 1955)
Following the Blind Leading the Blind
1997
Synthetic polymer and enamel paint on wood
144.6 × 142.6 × 29.8cm
National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne Purchased 1999
“The grid is a very peaceful thing, because nothing can go wrong … everything is complete. There is no room for anxiety … everything has a place. Everything is welcome.”
.
Louise Bourgeois
I had a weak-at-the-knees, tingle-all-over moment when I saw Louise Bourgeois’ work for the first time about fifteen years ago in Los Angeles. Yes I am a CRAZY fan. And, yes, it’s true I lay under her big spider in Tokyo and cried…
These are the releases I hope for in our vast world of art. Encounters when the artwork is somehow so inexplicably intimate, so beyond, so seemingly effortless that there can be no defence. In these moments there is an opening-up within the body, the mind, within all the senses … an experience of recognition, relief and awe that informs one’s deeper creative makeup.
.
Del Kathryn Barton
Del Kathryn Barton (Australian, b. 1972)
no other side
2012
(one part of nine)
Dupion silk and embroidery cotton
9 parts, each 42 × 45cm
In collaboration with Karen Barton
Courtesy of the artist and Roslyn Oxley9 Gallery, Sydney
“I guess every artist has other practices that they aspire to. Louise Bourgeois’ practice – by which I mean the combination of the works, the way that they were made, the artist and the way that she conducted herself – is such a practice for me. The way that she worked for so long, and continued to develop her work in good times and bad, as well as the way that her works are so much of their times but at the same time not quite in sync with them inspires me. The fact that I hardly know the work she made prior to her fifties demonstrates the truth of the idea that art is a lifetime project that can continue to evolve as an artist matures. And then, of course, there is the work itself.”
.
Patricia Piccinini
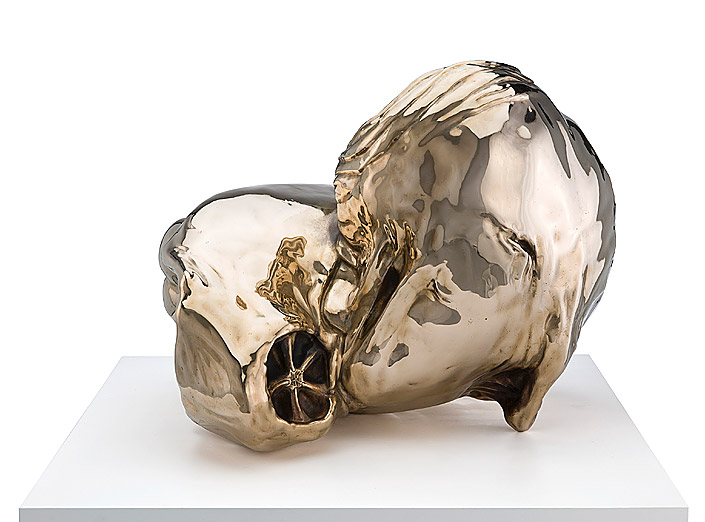
Patricia Piccinini (Australian, b. 1965)
The Uprising
2008
Bronze
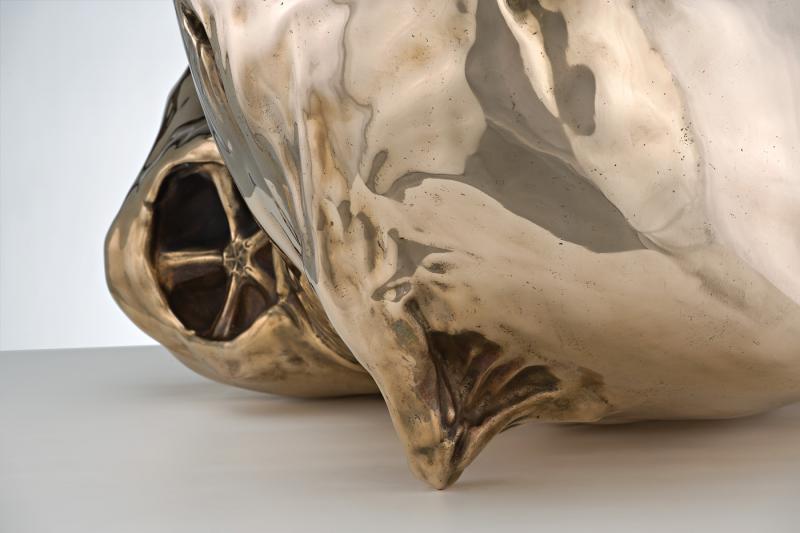
Patricia Piccinini (Australian, b. 1965)
The Uprising (detail)
2008
Bronze
“The massive aorta-like The Uprising, with its labyrinthine musculature, is a much stranger work. It establishes a bridge between the Vespa stags and the transgenic creatures, while being simultaneously amorphous and representational. Corporeal and mechanical, it suggests the plastic, porous, and uncertain world of the new nature that is at the core of the figurative works. For this reason it is physically sited at the boundary between natural history and art history…”
.
Juliana Engberg
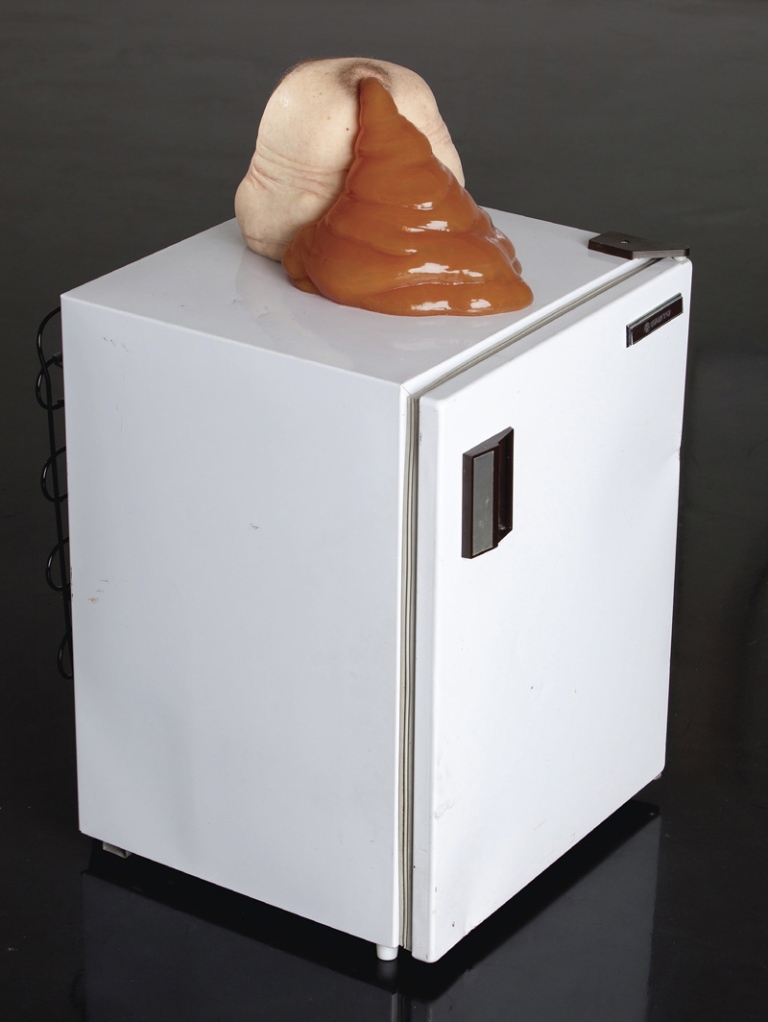
Patricia Piccinini (Australian, b. 1965)
Nectar
2012
Silicone, fibreglass, human hair, refrigerator edition 1/6
83 × 48 × 51cm
Courtesy of the artist, Tolarno Galleries, Melbourne, and Haunch of Venison, London and New York
“Taking her cue from the vague boundaries of the biotech world, ‘where it is difficult to figure exactly where the good becomes tainted and the bad becomes justifiable’, Piccinini considers her own hybrid creations, however abject or grotesque, as lovable, associated with fecundity, growth and optimism. Like Bourgeois, she presents strange couplings of the animal and the human, that despite their de-formations always convey intimacy and warmth. Here the title Nectar suggests that there may be something nourishing in what might otherwise appear as a failed experiment.”
Text from educational pdf
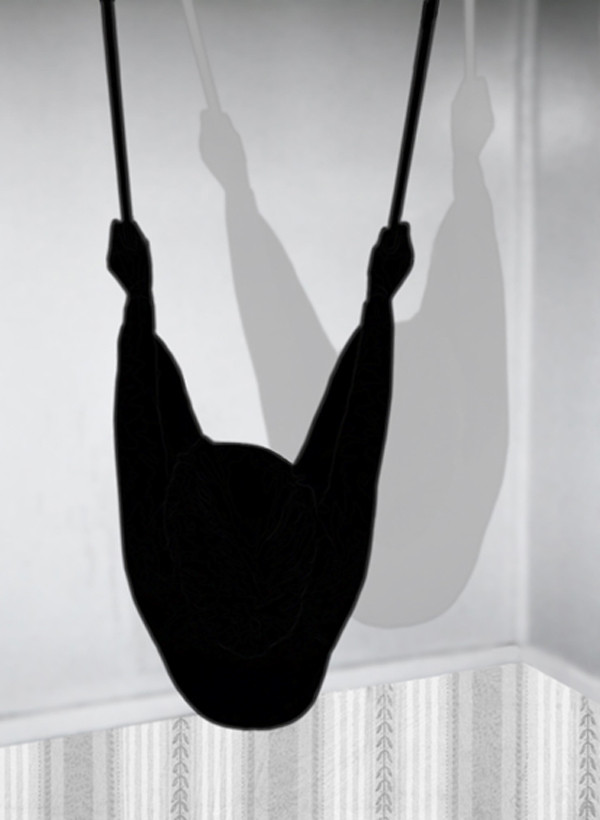
Pat Brassington (Australian, b. 1942)
House guest #2
2007
Pat Brassington (Australian, b. 1942)
The Guardian
2009
Pigment print on paper edition 6/8
112 × 87.5cm
Heide Museum of Modern Art, Melbourne
Purchased with funds from the Robert Salzer Foundation 2009
Louise Bourgeois at Heide Museum
A behind-the-scenes look at how the works of Louise Bourgeois, including her famous Spider were installed at Heide Museum.
Heide Museum of Modern Art
7, Templestowe Road
Bulleen, Victoria 3105
Opening hours:
(Heide II and Heide III)
Tuesday, Wednesday, Sunday, 10am – 5pm
Thursday – Saturday, 10am – 8pm
















You must be logged in to post a comment.