Accelerad

Description
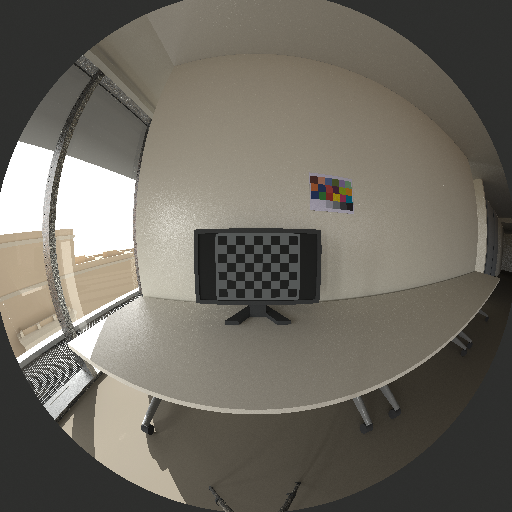
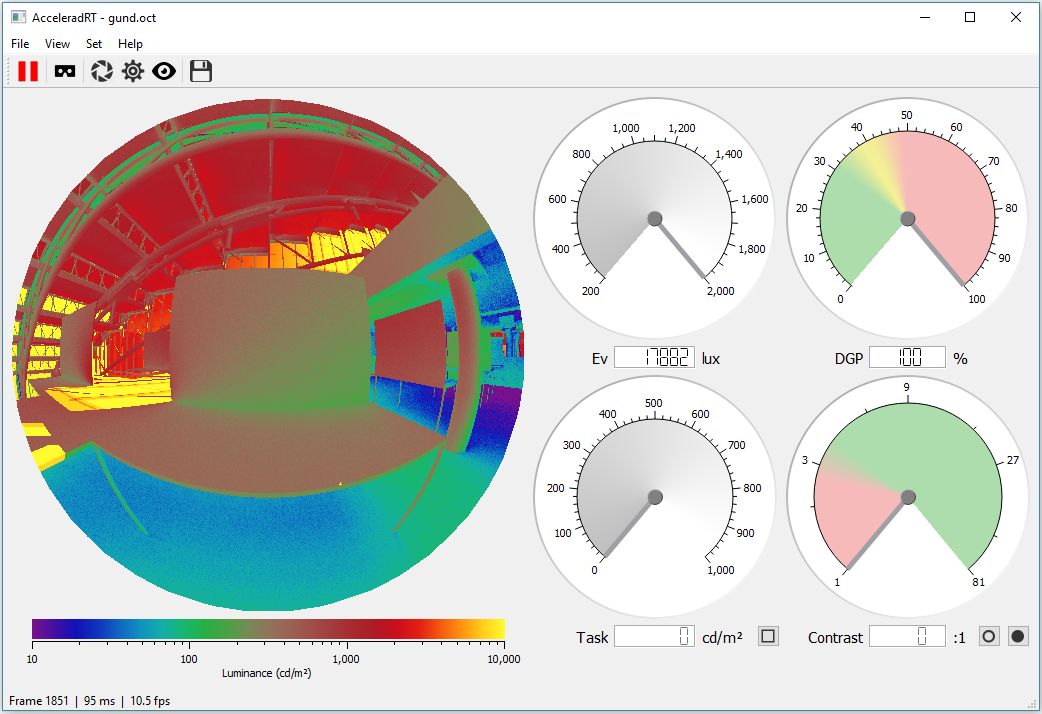
Accelerad is a free suite of programs for fast and accurate lighting and daylighting analysis and visualization. It was developed by Nathaniel Jones at the MIT Sustainable Design Lab and modeled after the popular Radiance software suite developed by Greg Ward at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. In order to allow for smooth adoption among Radiance users and software developers, Accelerad maintains compatibility with Radiance file formats, materials, and command-line arguments. Parallelism makes Accelerad up to forty times faster using OptiX™, a ray tracing engine built for the graphics processing unit (GPU). Accelerad is ideal for simulations that would be impractical to carry out on CPUs because of their size, such as renderings with large numbers of ambient bounces or grid-based calculations over many thousands of sensor points. It allows fast simulation of annual climate-based daylighting metrics through three-phase and five-phase simulations. An accompanying program, AcceleradRT, is an interactive interface for real-time daylighting, glare, and visual comfort analysis. AcceleradRT uses progressive path tracing to provide daylighitng simulation results in real time with validated accuracy. It includes AcceleradVR, an immersive visualization interface compatible with most virtual reality headsets.
