Serotonin
Serotonin
Reading time 2 min 11 sec
Speaking time 4 min 12 sec
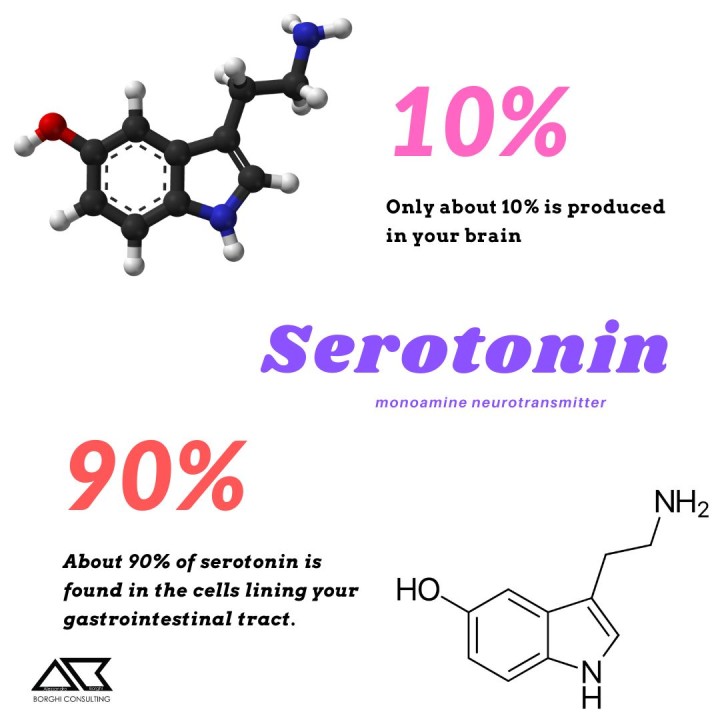
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter, a chemical messenger that plays an important role in regulating many bodily functions, including mood, appetite, and sleep. Serotonin is synthesized and released by specialized nerve cells in the brain and in the gut.
What is Serotonin?
Serotonin, also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter synthesized from the amino acid tryptophan. Serotonin is produced in specialized nerve cells called serotonergic neurons, which are located in the brainstem, and in the enterochromaffin cells of the gut. Serotonin is involved in many bodily functions, including:
- Mood regulation: Serotonin is often referred to as the "feel-good" neurotransmitter, as it is involved in regulating mood, reducing anxiety, and improving the overall sense of well-being.
- Appetite control: Serotonin plays a role in regulating appetite, as it helps to reduce cravings for carbohydrates and other foods.
- Sleep regulation: Serotonin is involved in regulating the sleep-wake cycle, promoting restful sleep and wakefulness during the day.
- Digestion: Serotonin is involved in regulating gut motility, and it helps to control the movement of food through the digestive system.
How is Serotonin Produced?
Serotonin is synthesized from the amino acid tryptophan, which is obtained from dietary sources. Tryptophan is converted to 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) by an enzyme called tryptophan hydroxylase. 5-HTP is then converted to serotonin by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase.
What Kind of Situations Can Trigger Serotonin Production?
There are several factors that can trigger the production of serotonin, including:
- Exposure to sunlight: Sunlight is a natural source of vitamin D, which is essential for serotonin production. Exposure to sunlight can also help to regulate the sleep-wake cycle, which is closely linked to serotonin production.
- Exercise: Physical activity can stimulate the production of serotonin, as well as other neurotransmitters that promote a sense of well-being.
- Meditation: Mindfulness practices such as meditation have been shown to increase serotonin production, leading to reduced anxiety and improved mood.
Brain Alterations Related to Serotonin
Low levels of serotonin have been associated with a number of mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), work by increasing the availability of serotonin in the brain, leading to improved mood and reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Mental Health Related to Serotonin
Serotonin plays a critical role in regulating mood, and low levels of serotonin have been associated with depression and anxiety. Some research suggests that people with depression may have lower levels of serotonin in the brain, although the relationship between serotonin and depression is complex and not fully understood.
Benefits of Meditation and Physical Activity
Meditation and physical activity have both been shown to increase serotonin production, leading to reduced anxiety and improved mood. Mindfulness practices such as meditation can help to reduce stress and improve emotional regulation, while physical activity can stimulate the production of serotonin and other feel-good neurotransmitters.
In conclusion, serotonin is a neurotransmitter that plays a critical role in regulating many bodily functions, including mood, appetite, and sleep. Serotonin is produced by specialized nerve cells in the brain and gut, and it is synthesized from the amino acid tryptophan. Factors such as exposure to sunlight, exercise, and mindfulness practices like meditation can all stimulate the production of serotonin, leading to reduced anxiety and improved mood.
Alessandro Borghi